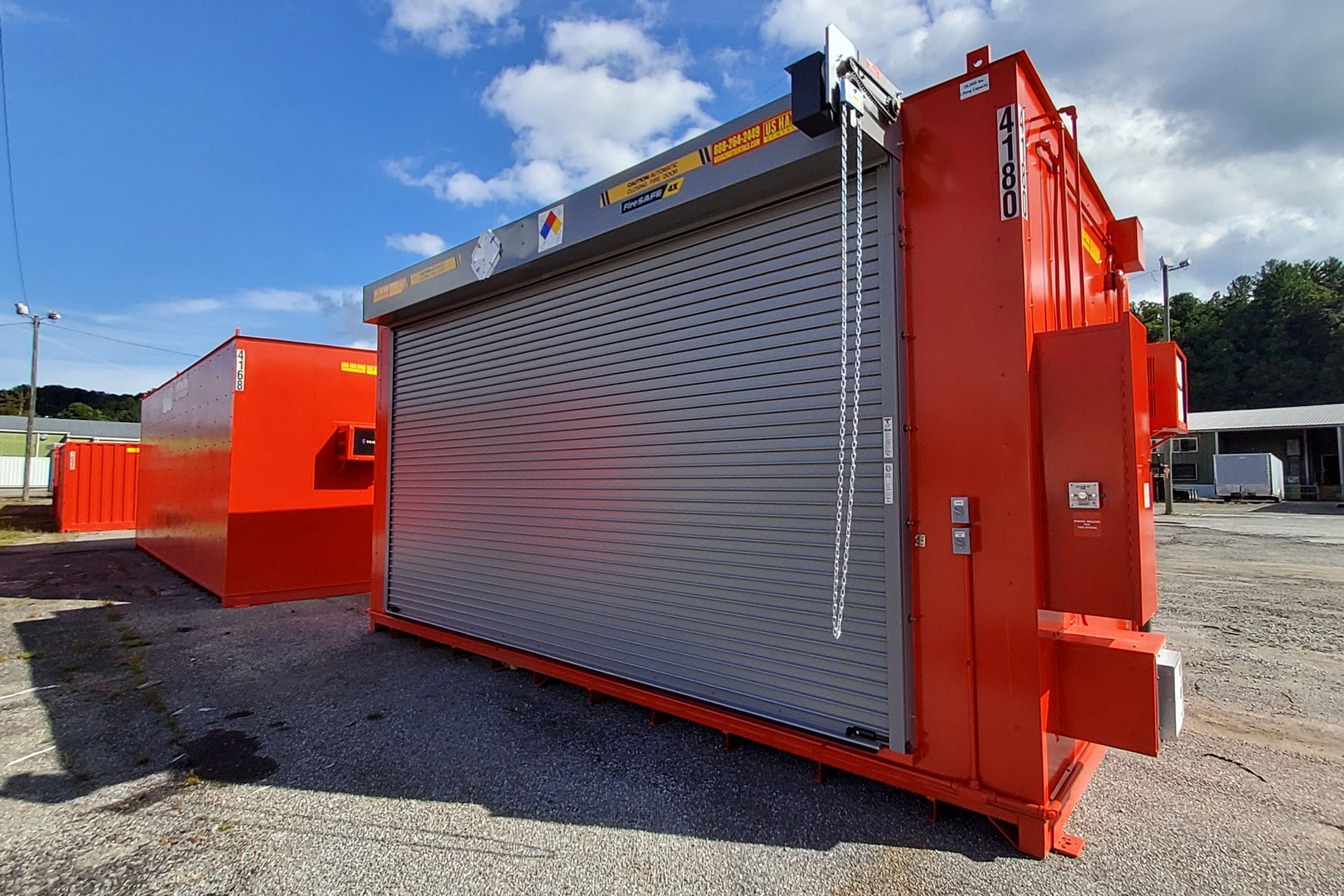
NFPA Hazard Label Identification & Rating System
The NFPA 704 Diamond is a standardized label created by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) to quickly and easily convey the hazards of chemicals and other hazardous materials. It is often referred to as the “fire diamond” because it is primarily used for emergency response situations, especially by firefighters and other emergency personnel. The label is designed to provide a simple, immediately recognizable, and easily understood method of conveying the general hazards of a material.

The NFPA 704 Diamond consists of a square divided into four smaller diamond-shaped sections, each with a specific color and representing a different type of hazard:
- Blue (Health Hazard): Located on the left side of the diamond. It indicates the level of health risk associated with the material. Ratings go from 0 (no hazard) to 4 (severe risk).
- Red (Flammability): Positioned at the top of the diamond. This section rates the material’s susceptibility to burning or catching fire, with ratings from 0 (will not burn) to 4 (extremely flammable).
- Yellow (Reactivity): On the right side of the diamond. This section assesses the chemical stability of the material and its potential for explosive reaction or release of hazardous energy. Ratings range from 0 (stable) to 4 (may detonate).
- White (Special Hazards): Found at the bottom of the diamond. Instead of a numerical rating, this section contains symbols to denote special hazards. Common symbols include “OX” for oxidizers, “W” for materials that are dangerous when wet, and “SA” for simple asphyxiants.
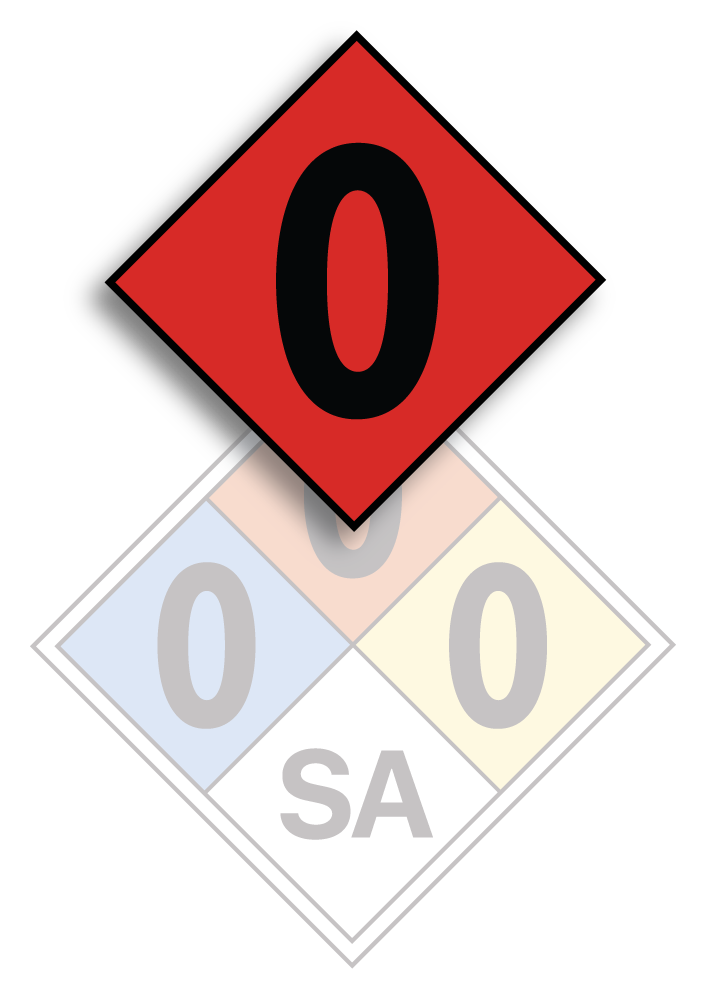
RED DIAMOND – NFPA Flammability Hazard Identification
- 0: Indicates that the material will not burn under typical fire conditions.
- 1: Suggests that the material requires considerable preheating before it will ignite.
- 2: Indicates that the material can ignite if moderately heated or exposed to high ambient temperatures.
- 3: This means that the material can ignite at most ambient temperatures, or that it can spontaneously heat up under normal conditions.
- 4: Represents materials that pose a severe risk because they readily vaporize at atmospheric pressure and normal temperatures, or they readily disperse in air and burn easily.
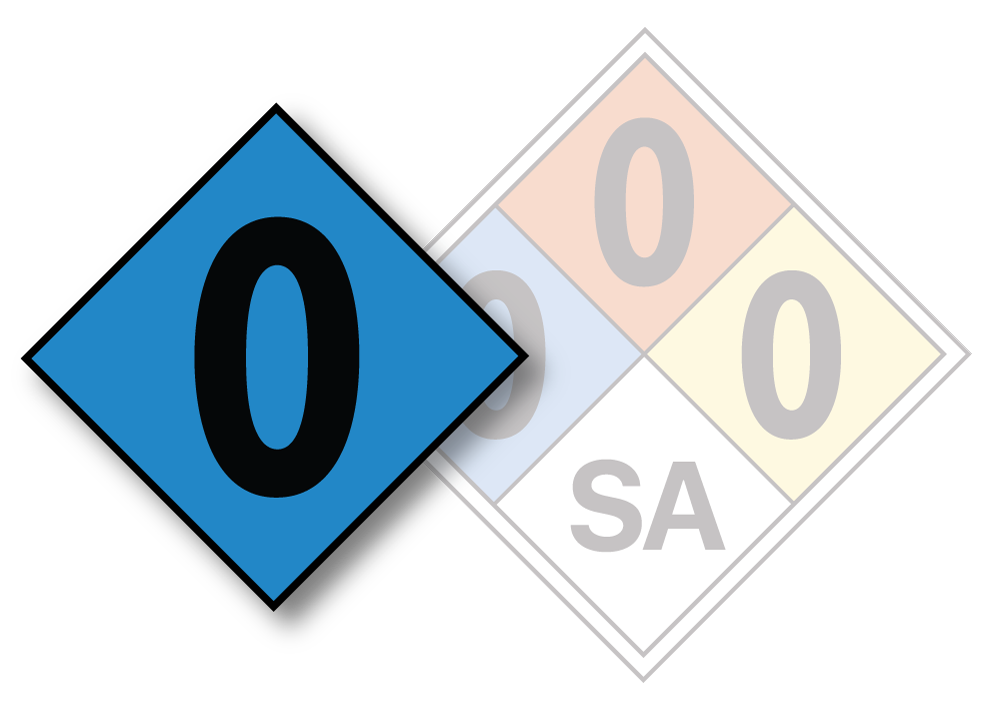
BLUE DIAMOND – NFPA Health Hazard Identification
The blue box in the NFPA Hazard Rating System label represents the health hazard of the material. This section is part of the NFPA 704 Diamond, which is a standardized system of labeling the hazards of materials for emergency response.
The health hazard ratings in the blue box are as follows:
- 0: Material poses no health hazard, no precautions are necessary, and there is little chance of injury.
- 1: Exposure would cause irritation but only minor residual injury.
- 2: Intense or continued exposure could cause temporary incapacitation or possible residual injury.
- 3: Short exposure could cause serious temporary or moderate residual injury.
- 4: Very short exposure could cause death or major residual injury.
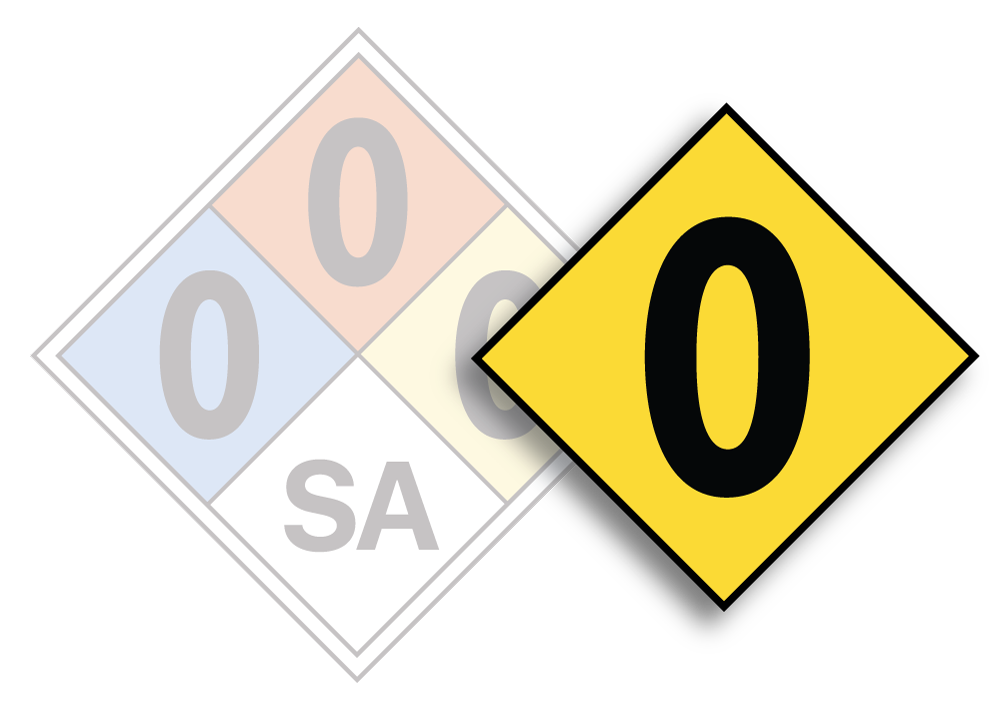
YELLOW DIAMOND – NFPA Chemical Stability Identification
- 0: Material is stable under most conditions.
- 1: Material is normally stable but can become unstable at elevated temperatures and pressures.
- 2: Material is unstable or may react violently under normal conditions. It may also react with water.
- 3: Material is capable of detonation or explosive decomposition but requires a strong initiating source or must be heated under confinement before initiation.
- 4: Material is readily capable of detonation or explosive decomposition at normal temperatures and pressures.
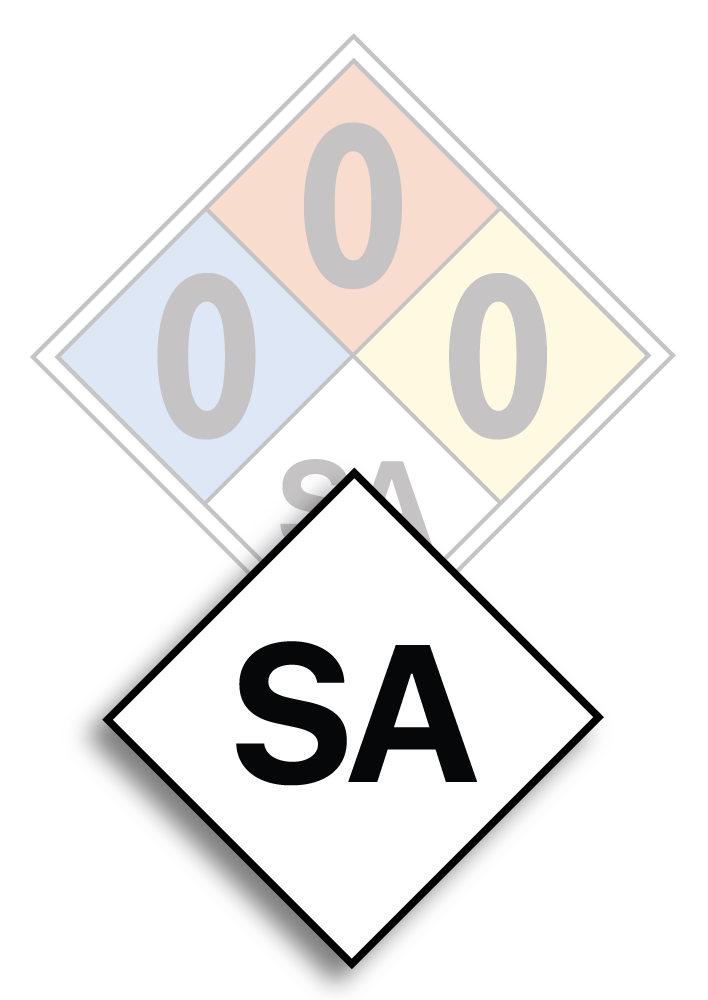
WHITE DIAMOND – NFPA Special Hazard Identification
- OX: Indicates that the material is an oxidizer. This means the substance can release oxygen to stimulate the combustion of other materials.
- W: Symbolizes that the material is water-reactive. When these substances come into contact with water, they may react violently or release a flammable gas.
- SA: Stands for simple asphyxiant. This is used for gases like nitrogen, helium, neon, argon, krypton, and xenon, which can displace oxygen in the air and pose an asphyxiation risk in confined spaces.
- BLANK: If no symbols are present, this signifies no specific additional hazards exist.
The inclusion of these symbols, when needed, provides crucial information for emergency responders. This helps them understand and anticipate the unique risks associated with potentially harmful, flammable, and hazardous chemicals when responding to a storage spill or an emergency situation.
Proper labeling and identification of materials stored in a containment area should be taken with great care and caution. Mislabeling the NFPA 704 Diamond could create great risk for workers and emergency responders when handling such materials or accessing these storage containment areas.
How does the NFPA 704 diamond hazard system apply to flammable material storage buildings?
The NFPA 704 Diamond hazard system is particularly relevant for the storage of flammable materials in buildings, as it provides essential information about the risks associated with these materials. Here’s how it applies to such storage facilities:
- Identification of Hazards: Each flammable material stored in the building should be clearly labeled with an NFPA 704 Diamond. This ensures that the flammability (red section), health (blue section), reactivity (yellow section), and any special hazards (white section) of each material are immediately identifiable.
- Risk Assessment and Planning: The ratings on the NFPA Diamonds help in assessing the overall risk profile of the facility. Knowing the specific hazards of each material aids in planning for safe storage, including considerations for fire suppression systems, ventilation, segregation of incompatible chemicals, and emergency response procedures.
- Location and Visibility of Labels: NFPA 704 labels should be placed in locations where they are easily visible to emergency responders and personnel. This is typically at entrances, on outside storage tanks, or on doors leading to storage areas.
- Emergency Response: In the event of an emergency, such as a fire, the NFPA 704 Diamond provides first responders with quick, crucial information about the types of hazards they might encounter, allowing for a more effective and safe response. This is particularly important for flammable materials, as the red section of the label will indicate the level of flammability risk.
- Compliance with Regulations: Using the NFPA 704 system in flammable material storage buildings often forms part of compliance with local fire codes and OSHA regulations. Facilities handling hazardous materials are typically required to have appropriate hazard communication standards in place, including labeling systems like NFPA 704.
- Training and Education: Workers and safety personnel in facilities storing flammable materials should be trained to understand and interpret NFPA 704 labels. This knowledge is crucial for daily safety practices and effective emergency response.
How does NFPA Hazard Identification and Classification relate to fire-rated storage?
- Hazard Identification and Classification: The NFPA 704 Diamond helps in identifying and classifying the hazards of materials stored within a facility, including their flammability (red section). This classification is crucial in determining the appropriate type of fire-rated storage needed to safely store these materials.
- Design and Construction of Storage Facilities: Fire-rated storage buildings or cabinets are designed and constructed to withstand fire for a specified period, typically rated in hours (e.g., 1-hour, 2-hour, or 4-hour fire rating). The hazard information provided by the NFPA 704 system can guide decisions on the required fire rating of storage units, ensuring that they are capable of containing fires involving the materials stored within them for a sufficient amount of time.
- Segregation of Incompatible Chemicals: The NFPA 704 Diamond indicates not only the flammability but also the reactivity of materials (yellow section). This information is vital for segregating incompatible chemicals within fire-rated storage to prevent accidental reactions that could lead to a fire or explosion.
- Emergency Response Planning: In the event of a fire, the NFPA 704 Diamond provides first responders with immediate information about the risks they face. This information, combined with the knowledge that materials are stored in fire-rated containers or areas, can significantly impact the tactics used by firefighters and the urgency of their response.
- Compliance with Safety Standards and Regulations: Both the NFPA 704 system and the use of fire-rated storage are often part of regulatory requirements for the storage of hazardous materials. While storing hazardous materials, compliance with NFPA, OSHA, EPA, and ATF standards are generally always required. These standards and storage guidance help ensure the safety of the facility, its employees, and emergency personnel. Please consult your local fire marshal or authority having jurisdiction for complete guidance concerning your onsite storage and compliance based on your local codes and specific facility locations and operations.
- Risk Reduction: By combining the hazard communication provided by the NFPA 704 system with the physical protection offered by fire-rated storage, and secondary spill containment systems, facilities significantly reduce the risk of fires and their potential impact. This comprehensive approach to safety helps protect property, the environment, and human life.
Understanding NFPA 170
NFPA 170 is a vital safety standard developed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) that delineates the symbols used for fire safety and emergency communications. These symbols play a crucial role in enhancing safety by ensuring clear and consistent visual communication, particularly in high-stress situations.
Purpose and Application
- Clarity in Communication: The symbols are designed to be universally recognized, aiding in quick comprehension and action during emergencies.
- Standardization Across Platforms: They are used in various formats, including signage, floor plans, and emergency diagrams, providing consistency across different safety documents and environments.
Key Features
- Comprehensive Symbol Set: It includes a wide array of symbols addressing different aspects of fire safety and emergencies, from evacuation routes to fire extinguisher locations.
- Adaptable Use: The standard applies to multiple sectors, ensuring that regardless of the industry—whether healthcare, commercial, or industrial—the symbols remain relevant and useful.
By providing a standardized visual language, NFPA 170 aids in fostering safer environments, allowing for rapid and effective communication during critical times.

In summary, the NFPA 704 Diamond system and fire-rated storage complement each other in the safe handling and storage of hazardous materials. The NFPA 704 system provides essential hazard information that informs the appropriate use and specification of fire-rated storage solutions, enhancing overall safety and compliance in facilities that handle flammable and hazardous materials.





