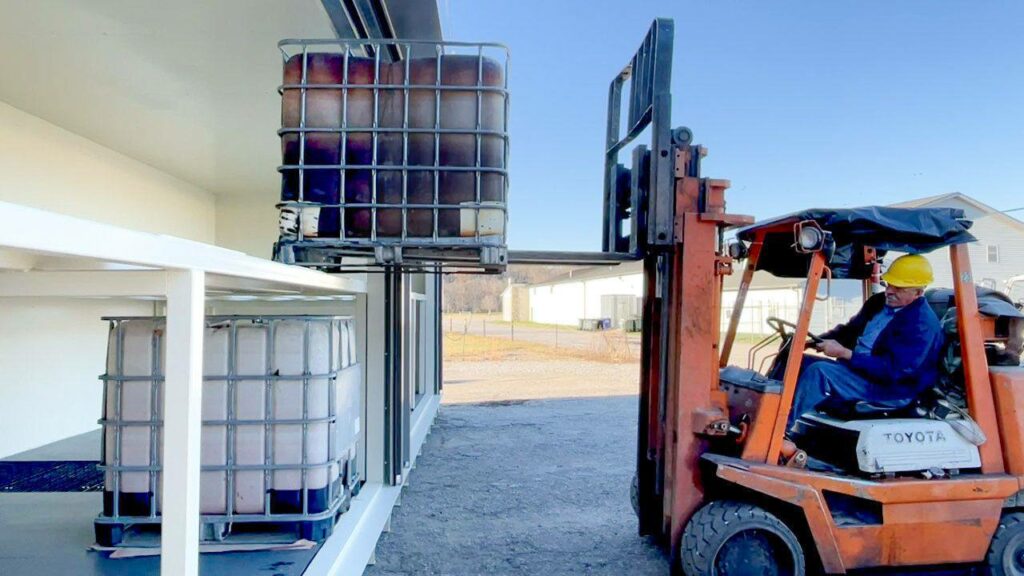
Hazardous waste generation is a common storage dilemma requiring a satellite accumulation area. Hazardous waste generation is any residual, toxic byproduct or waste originating from an industrial process that is harmful to health and the environment. Paints, solvents, motor oil, adhesives, batteries, sludge, and industrial cleaners are the most common examples of hazardous waste generation. Employees handling or responsible for hazardous waste generation also meet the requirement for industrial delineation. U.S. Hazmat’s Satellite Accumulation Area storage warehouses allow for the onsite production and storage of hazardous waste without needing a dangerous waste storage permit. These steel-welded storage conversion boxes with enhanced safety features meet OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.120 for storing hazardous waste and EPA Parts 261 and 263 storage requirements.
Proper Hazardous Waste Generation Storage
- Always accumulate or store waste close to the source, like in a steel drum, which can be stored in a SAA.
- Store waste in sturdy containers without rust or defects leading to leaks.
- Never store more than 55 gallons of hazardous waste at a time.
- Never store hazardous waste with incompatible materials.
- Always wear personal protective equipment when handling waste
- Only vent containers when necessary to operations.
- Keep hazardous waste container lids closed.
- Waste treatment is prohibited in SAAs.
- Only accumulate waste from routine operations in SAA.
- Develop storage protocols for improper mixing prevention.
- Lock doors and entry points for SAAs and secure drum lids.
- Designate key employees for hazardous waste custodial duties.
- Develop emergency preparedness plan for mitigating accidental releases.
SAA Advantages of Hazardous Waste Generation Operations
Laboratories, petroleum refining, industrial machining, wastewater treatment plants, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturers most commonly generate hazardous waste, but the list is not exhaustive. Almost every industry produces hazardous waste. With a growing emphasis on carbon neutrality and environmental stewardship, every industrial manufacturer should secure EPA and OSHA-compliant hazardous waste storage. Our SAA warehouses provide onsite temporary storage protection without interrupting workplace operations. Although hazardous waste generation can occur at various production levels, employees should deposit waste accumulation in containers near the generation point. Manufacturers can place a U.S. Hazmat’s SAA Hazardous Waste Storage Warehouses near impacted operations. Furthermore, our satellite accumulation area lockers allow manufacturers to accumulate hazardous waste for more than 90 or 180 days before transporting the waste to a central accumulation area.
Hazardous Waste Generation and Satellite Accumulation Area Spill Containment
An SAA can be as small as a segregated shelf or counter or as large as a room, work area, or storage locker. Companies should never store more than 55 gallons of hazardous waste in a designated SAA. Many industrial operators store hazardous waste in airtight drums or containers with closed lids. Inventory specialists and personnel should never store hazardous waste generation with incompatible materials. All drums containing hazardous waste should be properly labeled with legible writing. Although emergency preparedness and proper hazardous waste generation procedures mitigate most industrial accidents, no job site is immune to extenuating circumstances. That’s where spill containment becomes any manufacturer’s saving grace.

Each SAA Hazardous Waste Storage Locker Comes With a Bottom-Affixed Spill Sump Containment System. Spilled Hazardous Waste Falls Through the Flooring and into the Sump Until Safe Extraction, Ensuring Lasting Protection and Compliance. Each Sump Safely Contains 10 percent of the Total Hazardous Waste Volume. A High-Density 20-mil Polyethylene Liner Covers the Sump.